- 知识点:
- 环境准备
- CMS 功能
- 实现步骤
- Step 1: Create the database
- Step 2: Create the articles database table
- Step 3: Make a configuration file
- Step 4: Build the Article class
- Step 5: Write the front-end
index.phpscript - Step 6: Write the back-end
admin.phpscript - Step 7: Create the front-end templates
- Step 8: Create the back-end templates
- Step 9: Create the stylesheet and logo image
- All done!
这是一篇学习 “Build a CMS in an Afternoon with PHP and MySQL” 的笔记,目的是学习如何用 PHP + MySQL 进行简单的项目开发,为 PHP 代码审计打下基础。
原文:
Build a CMS in an Afternoon with PHP and MySQL
All code copyright Elated Communications Ltd 2011.
我把原文的代码敲了一遍,放在自己的 Github 里,叫做 mini-cms-article。除了学习用 PHP + MySQL 搭建一个简单的 CMS 之外,也是学习熟悉一些 Git 的操作。
知识点:
Along the way, you’ll learn how to create MySQL databases and tables; how to work with PHP objects, constants, includes, sessions, and other features; how to separate business logic from presentation; how to make your PHP code more secure, and much more!
- 创建数据库和数据库表
- 数据库查询、插入、更新、删除等
- PHP 对象、常量、包含、会话等
- 分离业务逻辑和页面展示
环境准备
For this tutorial, you’ll need to have the Apache web server with PHP installed, as well as the MySQL database server running on your computer.
关于 Apache + PHP + MySQL,Windows 下推荐用 phpStudy 或者 XAMPP。phpStudy 有个“站点域名管理”的功能,能够在不同目录,不同域名和端口下灵活部署多个站点。
PHP 版本:php-5.3.29-nts
MySQL 版本:5.5.53
CMS 功能
该 CMS 实现了简单的文章显示、编辑和管理功能,但是只有管理员 1 个账户,可以考虑增加多用户、文章评论等功能,类似博客。
前端:
- 主页,显示 5 篇最近的文章
- 文章列表页面,显示所有文章
- 文章查看页面,显示文章内容
后端:
- 管理登录和登出
- 列出所有文章
- 增加新的文章
- 编辑文章
- 删除文章
每篇文章列表会显示标题、摘要和发布时间。
实现步骤
- Create the database (articlescms)
- Create the articles database table (articles)
- Make a configuration file (config.php)
- Build the Article class (classes/Article.php)
- Write the front-end index.php script
- Write the back-end admin.php script
- Create the front-end templates
- Create the back-end templates
- Create the stylesheet and logo image
Ready? Grab a cup of coffee, and let’s get coding!
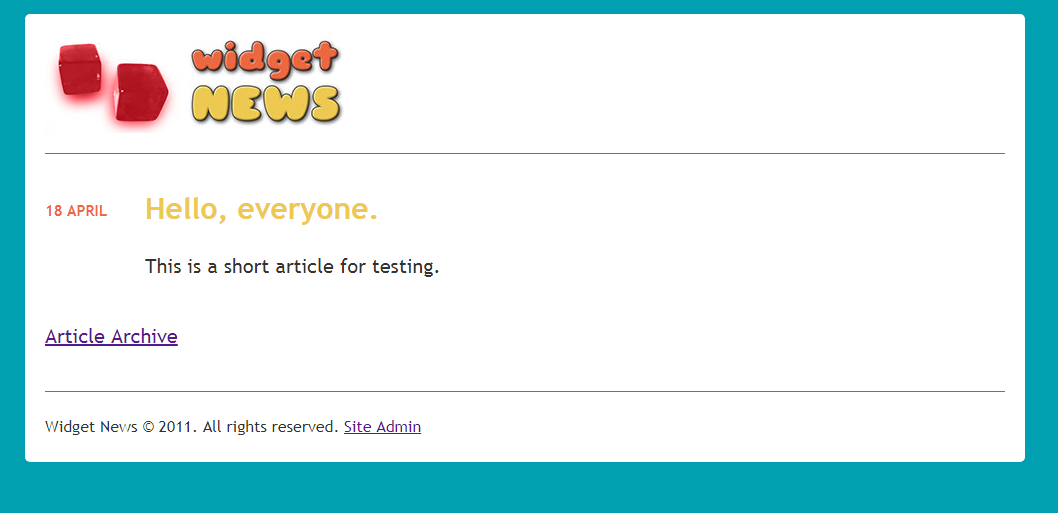
Step 1: Create the database
-
Run the mysql client program
C:\Users\Administrator λ mysql -u root -p Enter password: **** Welcome to the M ySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MySQL conne ction id i s 2 Server version: 5.5.53 MyS QL Community Server ( GPL) Copyright (c) 20 00, 2016, Or acle and/or its aff iliates. All rights reserved. Oracle is a r egistered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its affiliates. O ther names may be trademarks of their respective owners. Type 'h elp;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input stateme nt. mysql> -
Create the database
-
Quit the mysql client program
mysql> create database articlescms; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec) mysql> use articlescms; Database changed mysql> exit Bye
Step 2: Create the articles database table
- Create the articles table
- Give each article a unique ID
- Add the publicationDate field
- Add the title field
- Add the summary and content fields
- Add the primary key
articles 表的结构如下:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS articles;
CREATE TABLE articles
(
id smallint unsigned NOT NULL auto_increment,
publicationDate date NOT NULL, # When the article was published
title varchar(255) NOT NULL, # Full title of the article
summary text NOT NULL, # A short summary of the article
content mediumtext NOT NULL, # The HTML content of the article
PRIMARY KEY (id)
);
每篇文章包括 id,发布时间,标题,摘要,内容等 5 个属性。
id 为主键,类型为 smallint unsigned,值不能为空,值是唯一的,并自动增加。每个表只能有一个主键,用来标识表中的各项记录。
新建 tables.sql,内容如上表,在 articlescms 数据库中创建该表。
命令如下:
d:\myProjects
λ cd mini-cms-article\
d:\myProjects\mini-cms-article
λ ls tables.sql
tables.sql
d:\myProjects\mini-cms-article
λ mysql -u root -p
Enter password: ****
Welcome to the MySQL monitor.
...
mysql> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| articlescms |
| challenges |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| security |
| test |
| zvuldrill |
+--------------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> use articlescms;
Database changed
mysql> source tables.sql;
Query OK, 0 rows affected, 1 warning (0.31 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.08 sec)
mysql> desc articles;
+-----------------+----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| Field | Type | Null | Key | Default | Extra |
+-----------------+----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
| id | smallint(5) unsigned | NO | PRI | NULL | auto_increment |
| publicationDate | date | NO | | NULL | |
| title | varchar(255) | NO | | NULL | |
| summary | text | NO | | NULL | |
| content | mediumtext | NO | | NULL | |
+-----------------+----------------------+------+-----+---------+----------------+
5 rows in set (0.01 sec)
或者
d:\myProjects\mini-cms-article
λ mysql -u root -p articlescms < tables.sql
Enter password: ****
Step 3: Make a configuration file
配置文件存储一些设置,用于整个 CMS 的所有脚本。
- Display errors in the browser
- Set the timezones
- Set the database access details
- Set the paths
- Set the number of articles to display on the homepage
- Set the admin username and password
- Include the Article class
- Create an exception handler
<?php
ini_set( "display_errors", true ); // 在浏览器上显示错误信息。
date_default_timezone_set( "Asia/Shanghai" ); // 设置时区 http://www.php.net/manual/en/timezones.php
define( "DB_DSN", "mysql:host=localhost;dbname=articlescms" );
define( "DB_USERNAME", "username" );
define( "DB_PASSWORD", "password" );
define( "CLASS_PATH", "classes" );
define( "TEMPLATE_PATH", "templates" );
define( "HOMEPAGE_NUM_ARTICLES", 5 );
define( "ADMIN_USERNAME", "admin" );
define( "ADMIN_PASSWORD", "mypass" );
require( CLASS_PATH . "/Article.php" );
function handleException( $exception ) {
echo "Sorry, a problem occurred. Please try later.";
error_log( $exception->getMessage() );
}
set_exception_handler( 'handleException' );
?>
将数据库相关的参数改为自己 MySQL 的设置,包括数据库地址、名称、用户、密码等。
ADMIN_USERNAME 和 ADMIN_PASSWORD 为 CMS 管理员用户和密码。
Security note
In a live server environment it’d be a good idea to place config.php somewhere outside your website’s document root, since it contains usernames and passwords. While it’s not usually possible to read the source code of a PHP script via the browser, it does happen sometimes if the web server is misconfigured.
You could also use hash() to make a hash from your admin password, and store the hash in config.php instead of the plaintext password. Then, at login time, you can hash() the entered password and see if it matches the hash in config.php.
在 Web 的部署环境中,最好不好把配置文件放在网站目录下,除了采取 hash() 的方式外,最好是把管理员和密码放在服务器的环境变量里,在代码啊中不存放用户名和密码,需要时从环境变量里读取。而普通用户的密码一般是加密后存放在数据库里,用户登录验证的时候,从数据库读取相应值进行比较来完成验证。
Step 4: Build the Article class
Article 类是该 CMS 的核心,用于处理文章的所有操作,包括存储文章到数据库,从数据库获取文章,以及其他脚本用它来创建、更新、检索和删除文章。
-
The class definition and properties
class Article { // Properties /** * @var int The article ID from the database */ public $id = null; ... } -
The constructor
The first method,
__construct(), is the constructor. This is a special method that is called automatically by the PHP engine whenever a newArticleobject is created. Our constructor takes an optional$dataarray containing the data to put into the new object’s properties. We then populate those properties within the body of the constructor. This gives us a handy way to create and populate an object in one go.创建类的实例后,会首先调用类的构造函数,完成一些初始化的工作。
public function __construct( $data=array() ) { if ( isset( $data['id'] ) ) $this->id = (int) $data['id']; if ( isset( $data['publicationDate'] ) ) $this->publicationDate = (int) $data['publicationDate']; if ( isset( $data['title'] ) ) $this->title = preg_replace ( "/[^\.\,\-\_\'\"\@\?\!\:\$ a-zA-Z0-9()]/", "", $data['title'] ); if ( isset( $data['summary'] ) ) $this->summary = preg_replace ( "/[^\.\,\-\_\'\"\@\?\!\:\$ a-zA-Z0-9()]/", "", $data['summary'] ); if ( isset( $data['content'] ) ) $this->content = $data['content']; } -
storeFormValues()Sets the object’s properties using the edit form post values in the supplied array
通过用户提交的表单的数据,来设置 Article 类对象的属性。
-
getById()Returns an Article object matching the given article ID
$sql = "SELECT *, UNIX_TIMESTAMP(publicationDate) AS publicationDate FROM articles WHERE id = :id";通过文章的 ID 属性来获取 Article 对象的其他属性,这里返回的是一个新的 Article 对象。
-
getList()Returns all (or a range of) Article objects in the DB
$sql = "SELECT SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS *, UNIX_TIMESTAMP(publicationDate) AS publicationDate FROM articles ORDER BY " . mysql_escape_string($order) . " LIMIT :numRows";获取数据库中所有的 Article 对象。
-
insert()Inserts the current Article object into the database, and sets its ID property.
$sql = "INSERT INTO articles ( publicationDate, title, summary, content ) VALUES ( FROM_UNIXTIME(:publicationDate), :title, :summary, :content )";插入新的 Article 对象到数据库,这里的 ID 属性会自动增加。
-
update()Updates the current Article object in the database.
$sql = "UPDATE articles SET publicationDate=FROM_UNIXTIME(:publicationDate), title=:title, summary=:summary, content=:content WHERE id = :id";更新数据库中当前的 Article 对象。
-
delete()Deletes the current Article object from the database.
"DELETE FROM articles WHERE id = :id LIMIT 1"从数据库里删除当前的 Article 对象。
<?php
/**
* Class to handle articles
*/
class Article
{
// Properties
/**
* @var int The article ID from the database
*/
public $id = null;
/**
* @var int When the article is to be / was first published
*/
public $publicationDate = null;
/**
* @var string Full title of the article
*/
public $title = null;
/**
* @var string A short summary of the article
*/
public $summary = null;
/**
* @var string The HTML content of the article
*/
public $content = null;
/**
* Sets the object's properties using the values in the supplied array
*
* @param assoc The property values
*/
public function __construct( $data=array() ) {
if ( isset( $data['id'] ) ) $this->id = (int) $data['id'];
if ( isset( $data['publicationDate'] ) ) $this->publicationDate = (int) $data['publicationDate'];
if ( isset( $data['title'] ) ) $this->title = preg_replace ( "/[^\.\,\-\_\'\"\@\?\!\:\$ a-zA-Z0-9()]/", "", $data['title'] );
if ( isset( $data['summary'] ) ) $this->summary = preg_replace ( "/[^\.\,\-\_\'\"\@\?\!\:\$ a-zA-Z0-9()]/", "", $data['summary'] );
if ( isset( $data['content'] ) ) $this->content = $data['content'];
}
/**
* Sets the object's properties using the edit form post values in the supplied array
*
* @param assoc The form post values
*/
public function storeFormValues ( $params ) {
// Store all the parameters
$this->__construct( $params );
// Parse and store the publication date
if ( isset($params['publicationDate']) ) {
$publicationDate = explode ( '-', $params['publicationDate'] );
if ( count($publicationDate) == 3 ) {
list ( $y, $m, $d ) = $publicationDate;
$this->publicationDate = mktime ( 0, 0, 0, $m, $d, $y );
}
}
}
/**
* Returns an Article object matching the given article ID
*
* @param int The article ID
* @return Article|false The article object, or false if the record was not found or there was a problem
*/
public static function getById( $id ) {
$conn = new PDO( DB_DSN, DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD );
$sql = "SELECT *, UNIX_TIMESTAMP(publicationDate) AS publicationDate FROM articles WHERE id = :id";
$st = $conn->prepare( $sql );
$st->bindValue( ":id", $id, PDO::PARAM_INT );
$st->execute();
$row = $st->fetch();
$conn = null;
if ( $row ) return new Article( $row );
}
/**
* Returns all (or a range of) Article objects in the DB
*
* @param int Optional The number of rows to return (default=all)
* @param string Optional column by which to order the articles (default="publicationDate DESC")
* @return Array|false A two-element array : results => array, a list of Article objects; totalRows => Total number of articles
*/
public static function getList( $numRows=1000000, $order="publicationDate DESC" ) {
$conn = new PDO( DB_DSN, DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD );
$sql = "SELECT SQL_CALC_FOUND_ROWS *, UNIX_TIMESTAMP(publicationDate) AS publicationDate FROM articles
ORDER BY " . mysql_escape_string($order) . " LIMIT :numRows";
$st = $conn->prepare( $sql );
$st->bindValue( ":numRows", $numRows, PDO::PARAM_INT );
$st->execute();
$list = array();
while ( $row = $st->fetch() ) {
$article = new Article( $row );
$list[] = $article;
}
// Now get the total number of articles that matched the criteria
$sql = "SELECT FOUND_ROWS() AS totalRows";
$totalRows = $conn->query( $sql )->fetch();
$conn = null;
return ( array ( "results" => $list, "totalRows" => $totalRows[0] ) );
}
/**
* Inserts the current Article object into the database, and sets its ID property.
*/
public function insert() {
// Does the Article object already have an ID?
if ( !is_null( $this->id ) ) trigger_error ( "Article::insert(): Attempt to insert an Article object that already has its ID property set (to $this->id).", E_USER_ERROR );
// Insert the Article
$conn = new PDO( DB_DSN, DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD );
$sql = "INSERT INTO articles ( publicationDate, title, summary, content ) VALUES ( FROM_UNIXTIME(:publicationDate), :title, :summary, :content )";
$st = $conn->prepare ( $sql );
$st->bindValue( ":publicationDate", $this->publicationDate, PDO::PARAM_INT );
$st->bindValue( ":title", $this->title, PDO::PARAM_STR );
$st->bindValue( ":summary", $this->summary, PDO::PARAM_STR );
$st->bindValue( ":content", $this->content, PDO::PARAM_STR );
$st->execute();
$this->id = $conn->lastInsertId();
$conn = null;
}
/**
* Updates the current Article object in the database.
*/
public function update() {
// Does the Article object have an ID?
if ( is_null( $this->id ) ) trigger_error ( "Article::update(): Attempt to update an Article object that does not have its ID property set.", E_USER_ERROR );
// Update the Article
$conn = new PDO( DB_DSN, DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD );
$sql = "UPDATE articles SET publicationDate=FROM_UNIXTIME(:publicationDate), title=:title, summary=:summary, content=:content WHERE id = :id";
$st = $conn->prepare ( $sql );
$st->bindValue( ":publicationDate", $this->publicationDate, PDO::PARAM_INT );
$st->bindValue( ":title", $this->title, PDO::PARAM_STR );
$st->bindValue( ":summary", $this->summary, PDO::PARAM_STR );
$st->bindValue( ":content", $this->content, PDO::PARAM_STR );
$st->bindValue( ":id", $this->id, PDO::PARAM_INT );
$st->execute();
$conn = null;
}
/**
* Deletes the current Article object from the database.
*/
public function delete() {
// Does the Article object have an ID?
if ( is_null( $this->id ) ) trigger_error ( "Article::delete(): Attempt to delete an Article object that does not have its ID property set.", E_USER_ERROR );
// Delete the Article
$conn = new PDO( DB_DSN, DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD );
$st = $conn->prepare ( "DELETE FROM articles WHERE id = :id LIMIT 1" );
$st->bindValue( ":id", $this->id, PDO::PARAM_INT );
$st->execute();
$conn = null;
}
}
?>
关于对输入数据的检查
在构造函数中,对 title 和 summary 变量进行了过滤,避免一些恶意的数据进入数据库,采取的是正则的方式来过滤变量输入。关于正则的内容,还要仔细的学习下。
- You’ll notice that the method filters the data before it stores them in the properties. The
idandpublicationDateproperties are cast to integers using(int), since these values should always be integers. Thetitleandsummaryare filtered using a regular expression to only allow a certain range of characters. It’s good security practice to filter data on input like this, only allowing acceptable values and characters through.- We don’t filter the
contentproperty, however. Why? Well, the administrator will probably want to use a wide range of characters, as well as HTML markup, in the article content. If we restricted the range of allowed characters in the content then we would limit the usefulness of the CMS for the administrator.- Normally this could be a security loophole, since a user could insert malicious JavaScript and other nasty stuff in the content. However, since we presumably trust our site administrator — who is the only person allowed to create the content — this is an acceptable tradeoff in this case. If you were dealing with user-generated content, such as comments or forum posts, then you would want to be more careful, and only allow “safe” HTML to be used. A really great tool for this is HTML Purifier, which thoroughly analyses HTML input and removes all potentially malicious code.
- PHP security is a big topic, and beyond the scope of this tutorial. If you’d like to find out more then start with Terry Chay’s excellent post, Filter Input-Escape Output: Security Principle and Practice. Also see the Wikipedia entries on secure input/output handling, XSS, CSRF, SQL injection, and session fixation.
关于数据库连接
这里使用 PDO 连接数据库。
$conn = new PDO( DB_DSN, DB_USERNAME, DB_PASSWORD );
$sql = "SELECT *, UNIX_TIMESTAMP(publicationDate) AS publicationDate FROM articles WHERE id = :id";
$st = $conn->prepare( $sql );
$st->bindValue( ":id", $id, PDO::PARAM_INT );
$st->execute();
$row = $st->fetch();
PDO — PHP Data Objects — is an object-oriented library built into PHP that makes it easy for PHP scripts to talk to databases.
使用 PDO 可以很好的解决 SQL 注入的问题,在 sql 语句中,会先用占位符来代替条件语句中的参数值,后续用 bindValue() 来赋值和检测,最后再对数据库执行 sql 操作。
Our
SELECTstatement retrieves all fields (*) from the record in thearticlestable that matches the givenidfield. It also retrieves thepublicationDatefield in UNIX timestamp format instead of the default MySQL date format, so we can store it easily in our object.Rather than placing our
$idparameter directly inside theSELECTstring, which can be a security risk, we instead use:id. This is known as a placeholder. In a minute, we’ll call a PDO method to bind our$idvalue to this placeholder.Once we’ve stored our
SELECTstatement in a string, we prepare the statement by calling$conn->prepare(), storing the resulting statement handle in a$stvariable.We now bind the value of our
$idvariable — that is, the ID of the article we want to retrieve — to our:idplaceholder by calling thebindValue()method. We pass in the placeholder name; the value to bind to it; and the value’s data type (integer in this case) so that PDO knows how to correctly escape the value.Lastly, we call
execute()to run the query, then we usefetch()to retrieve the resulting record as an associative array of field names and corresponding field values, which we store in the$rowvariable.
关于类的成员,即属性和方法:
All of the members (that is, the properties and methods) of our
Articleclass have thepublickeyword before their names, which means that they’re available to code outside the class. You can also createprivatemembers (which can only be used by the class itself) andprotectedmembers (which can be used by the class and any of its subclasses).
另外,Article 类有两个成员函数加了 static 来修饰。有了 static 后,这两个函数可以直接通过类来调用,而不用先创建类实例。
public static function getById( $id ) {
...
}
public static function getList( $numRows=1000000, $order="publicationDate DESC" ) {
...
}
// 在 index.php 里,有直接通过类调用的代码。
$data = Article::getList();
$results['article'] = Article::getById( (int)$_GET["articleId"] );
Step 5: Write the front-end index.php script
- Include the config file
- Grab the action parameter
- Decide which action to perform
archive()viewArticle()homepage()
<?php
/*
We use require() rather than include(); require() generates an error if the file can't be found.
*/
require( "config.php" );
/*
It's good programming practice to check that user-supplied values, such as query string parameters, form post values and cookies, actually exist before attempting to use them. Not only does it limit security holes, but it prevents the PHP engine raising "undefined index" notices as your script runs.
*/
$action = isset( $_GET['action'] ) ? $_GET['action'] : "";
switch ( $action ) {
case 'archive':
archive();
break;
case 'viewArticle':
viewArticle();
break;
default:
homepage();
}
function archive() {
$results = array();
$data = Article::getList();
$results['articles'] = $data['results'];
$results['totalRows'] = $data['totalRows'];
$results['pageTitle'] = "Article Archive | Widget News";
require( TEMPLATE_PATH . "/archive.php" );
}
function viewArticle() {
if ( !isset($_GET["articleId"]) || !$_GET["articleId"] ) {
homepage();
return;
}
$results = array();
$results['article'] = Article::getById( (int)$_GET["articleId"] );
$results['pageTitle'] = $results['article']->title . " | Widget News";
require( TEMPLATE_PATH . "/viewArticle.php" );
}
function homepage() {
$results = array();
$data = Article::getList( HOMEPAGE_NUM_ARTICLES );
$results['articles'] = $data['results'];
$results['totalRows'] = $data['totalRows'];
$results['pageTitle'] = "Widget News";
require( TEMPLATE_PATH . "/homepage.php" );
}
?>
Step 6: Write the back-end admin.php script
-
Start a user session
Towards the top of the script we call
session_start(). This PHP function starts a new session for the user, which we can use to track whether the user is logged in or not. (If a session for this user already exists, PHP automatically picks it up and uses it.)Because sessions need cookies to work, and cookies are sent to the browser before content, you should call
session_start()at the top of the script, before any content has been output.session_start()函数一般要放在其他代码之前。因为会话要基于 cookies 来工作,而 cookies 要在其他内容交互之前进行传输。 -
Grab the
actionparameter andusernamesession session variable -
Check the user is logged in
-
Decide which action to perform
-
login()If the user has submitted the login form — which we check by looking for the
loginform parameter — then the function checks the entered username and password against the config valuesADMIN_USERNAMEandADMIN_PASSWORD. If they match then theusernamesession key is set to the admin username,这里只是把用户提交的表单数据和 config.php 里的设置进行简单比较来完成验证。
-
logout()It simply removes the
usernamesession key.unset( $_SESSION['username'] ); -
newArticle() -
editArticle() -
deleteArticle() -
listArticles()
<?php
require( "config.php" );
session_start();
$action = isset( $_GET['action'] ) ? $_GET['action'] : "";
$username = isset( $_SESSION['username'] ) ? $_SESSION['username'] : "";
if ( $action != "login" && $action != "logout" && !$username ) {
login();
exit;
}
switch ( $action ) {
case 'login':
login();
break;
case 'logout':
logout();
break;
case 'newArticle':
newArticle();
break;
case 'editArticle':
editArticle();
break;
case 'deleteArticle':
deleteArticle();
break;
default:
listArticles();
}
function login() {
$results = array();
$results['pageTitle'] = "Admin Login | Widget News";
if ( isset( $_POST['login'] ) ) {
// User has posted the login form: attempt to log the user in
if ( $_POST['username'] == ADMIN_USERNAME && $_POST['password'] == ADMIN_PASSWORD ) {
// Login successful: Create a session and redirect to the admin homepage
$_SESSION['username'] = ADMIN_USERNAME;
header( "Location: admin.php" );
} else {
// Login failed: display an error message to the user
$results['errorMessage'] = "Incorrect username or password. Please try again.";
require( TEMPLATE_PATH . "/admin/loginForm.php" );
}
} else {
// User has not posted the login form yet: display the form
require( TEMPLATE_PATH . "/admin/loginForm.php" );
}
}
function logout() {
unset( $_SESSION['username'] );
header( "Location: admin.php" );
}
function newArticle() {
$results = array();
$results['pageTitle'] = "New Article";
$results['formAction'] = "newArticle";
if ( isset( $_POST['saveChanges'] ) ) {
// User has posted the article edit form: save the new article
$article = new Article;
$article->storeFormValues( $_POST );
$article->insert();
header( "Location: admin.php?status=changesSaved" );
} elseif ( isset( $_POST['cancel'] ) ) {
// User has cancelled their edits: return to the article list
header( "Location: admin.php" );
} else {
// User has not posted the article edit form yet: display the form
$results['article'] = new Article;
require( TEMPLATE_PATH . "/admin/editArticle.php" );
}
}
function editArticle() {
$results = array();
$results['pageTitle'] = "Edit Article";
$results['formAction'] = "editArticle";
if ( isset( $_POST['saveChanges'] ) ) {
// User has posted the article edit form: save the article changes
if ( !$article = Article::getById( (int)$_POST['articleId'] ) ) {
header( "Location: admin.php?error=articleNotFound" );
return;
}
$article->storeFormValues( $_POST );
$article->update();
header( "Location: admin.php?status=changesSaved" );
} elseif ( isset( $_POST['cancel'] ) ) {
// User has cancelled their edits: return to the article list
header( "Location: admin.php" );
} else {
// User has not posted the article edit form yet: display the form
$results['article'] = Article::getById( (int)$_GET['articleId'] );
require( TEMPLATE_PATH . "/admin/editArticle.php" );
}
}
function deleteArticle() {
if ( !$article = Article::getById( (int)$_GET['articleId'] ) ) {
header( "Location: admin.php?error=articleNotFound" );
return;
}
$article->delete();
header( "Location: admin.php?status=articleDeleted" );
}
function listArticles() {
$results = array();
$data = Article::getList();
$results['articles'] = $data['results'];
$results['totalRows'] = $data['totalRows'];
$results['pageTitle'] = "All Articles";
if ( isset( $_GET['error'] ) ) {
if ( $_GET['error'] == "articleNotFound" ) $results['errorMessage'] = "Error: Article not found.";
}
if ( isset( $_GET['status'] ) ) {
if ( $_GET['status'] == "changesSaved" ) $results['statusMessage'] = "Your changes have been saved.";
if ( $_GET['status'] == "articleDeleted" ) $results['statusMessage'] = "Article deleted.";
}
require( TEMPLATE_PATH . "/admin/listArticles.php" );
}
?>
以上 6 个步骤,就完成了 CMS 主要功能的 PHP 代码。下面的步骤就是创建前端显示的模板、样式,以及页面等文件。
这里的后端到前端的交互,主要是通过 $results 这个数组变量来进行,把后端的业务功能数据,通过该变量在前端页面上显示出来。前端到后端的交互,主要是通过 $_GET['xxx'] $_POST['xxx'] $_SESSION['xxx'] 等超全局变量,把前端 URL 地址栏变量,表单数据等传给后端来处理。
HTML 的代码不贴了,这里的前后端交互方式是有点落后吗?比如 header.php 和 footer.php 拼接在一起组成一个页面? HTML 和 php 代码在一起有没有更好的组织方式?还有就是什么是 MVC,什么是 REST 风格,后续有时间的话再深入学习下。
Step 7: Create the front-end templates
- The include files
- homepage.php
- archive.php
- viewArticle.php
Step 8: Create the back-end templates
- loginForm.php
- listArticles.php
- editArticle.php
As usual, we pass all data through
htmlspecialchars()before outputting it in the markup. Not only is this a good security habit, but it also ensures that our form field values are properly escaped. For example, if thetitlefield value contained a double quote (") that wasn’t escaped then the title would be truncated, since double quotes are used to delimit the field’s value in the markup.
htmlspecialchars() 函数,会将特殊字符转换为 HTML 实体,某类字符在 HTML 中有特殊用处,如需保持原意,需要用 HTML 实体来表达。 该函数会返回字符转义后的表达。比如一些字符转义后的值如下表:
| 字 符 | 替换后 |
|---|---|
& (& 符号) |
& |
" (双引号) |
",除非设置了 ENT_NOQUOTES |
' (单引号) |
设置了 ENT_QUOTES 后, ' (如果是 ENT_HTML401) ,或者 ' (如果是 ENT_XML1、 ENT_XHTML 或 ENT_HTML5)。 |
< (小于) |
< |
> (大于) |
> |
htmlspecialchars() 使得 HTML 之中的特殊字符被正确的编码,从而不会被使用者在页面注入 HTML 标签或者 Javascript 代码。
Step 9: Create the stylesheet and logo image
见 style.css
All done!
In this tutorial you’ve built a basic content management system from the ground up, using PHP and MySQL. You’ve learnt about MySQL, tables, field types, PDO, object-oriented programming, templating, security, sessions, and lots more.
While this CMS is pretty basic, it has hopefully given you a starting point for building your own CMS-driven websites. Some features you might want to add include:
- Pagination on the article archive (front end) and article list (back end) so that the system can easily handle hundreds of articles
- A WYSIWYG editor for easier content editing
- An image upload facility (I’ve written a follow-up tutorial on adding an image upload feature to the CMS)
- A preview facility, so the admin can see how an article will look before publishing it
- Article categories and tags (I’ve written a follow-up tutorial on adding categories)
- Integration with Apache’s mod_rewrite to create more human-friendly permalink URLs for the articles (find out how to do this)
- A user comments system
- I hope you’ve enjoyed this tutorial and found it useful. Happy coding!
可以进一步增加的内容:
- 分页功能
- 编辑器功能
- 图片上传功能
- 预览功能
- 文章分类和标签功能
- 评论功能
该文章讲得非常详细,非常适合入门学习,值得多读几遍,最好能码一遍代码。